- Section Nephrogenetics (AG Simons)
- Seniorprofessorship Prof. Rappold
- Molecular Neurogenetics (AG Berkel)
- Cardiogenetics (AG Hoffmann)
- Neurogastrogenetics
- Transcriptional regulation in developmental disorders (AG Laugsch)
- Genetics of neurodevelopmental disorders (AG Schaaf)
- Mouse models for neurodevelopmental disorders
- Research in our Diagnostic Laboratories
- Publications
Cardiogenetics (RG Hoffmann)
Research Group

Annette Löwen (MTA); Kristin Rädecke (PhD student); Ambuj Gore (MSc student); Sandra Hoffmann (Group Leader) (from left to right)
Research Focus
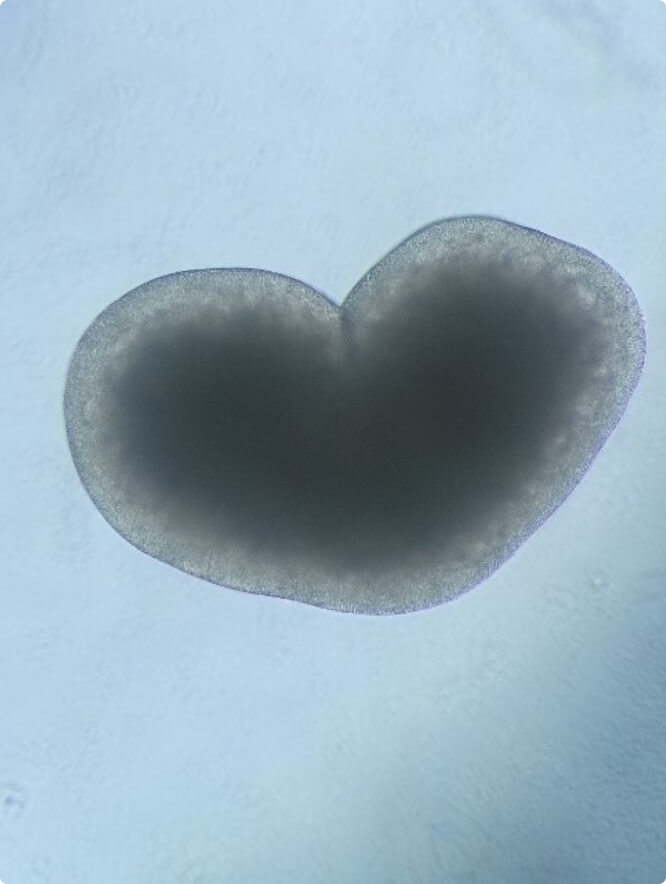
The heart’s rhythm is initiated and regulated by a population of specialized cells in the sinoatrial node, the natural pacemaker of the heart. Cardiac arrhythmias are pathological abnormalities from the normal heartbeat and are among the most common heart diseases.
In the last few years, transcription factors and their targets have been shown to play important roles in the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation, the most common cardiac arrhythmia, indicating that dysregulated gene expression is an essential underlying mechanism. Yet, our knowledge on gene regulatory networks associated with atrial fibrillation remains limited. Based on previous analysis, we have established a functional link between the expression of the homeodomain transcription factor SHOX2, the development of the sinoatrial node and arrhythmogenic phenotypes including atrial fibrillation and sinus node dysfunction.
Since the risk for atrial arrhythmias is defined by genetic alterations, we are highly interested in elucidating the underlying genetic networks and processes using state-of-the-art methods. We are applying different model systems and technologies including animal models (transgenic mice, zebrafish), patient material and pluripotent stem cells (patient-specific iPSCs, mouse ESCs) combined with cellular and molecular biological approaches, genome-editing (CRISPR-Cas9), genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic tools.
Modelling atrial arrhythmias with genotype-guided approaches using iPSCs will improve our understanding of the molecular mechanisms by which genomic variation cause those diseases. Moreover, these approaches provide a preclinical model for the selection of novel therapeutic targets, paving the way to personalized medicine.
Group Leader

Publications
Identification and Tissue-Specific Characterization of Novel SHOX-Regulated Genes in Zebrafish Highlights SOX Family Members Among Other Genes.
S. Hoffmann, R. Roeth, S. Diebold, J. Gogel, D. Hassel, S. Just, G. A. Rappold.
Front. Genet.. 2021 May 27;12. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.688808.
Network-driven discovery yields new insight into Shox2-dependent cardiac rhythm control.
S. Hoffmann, S. Schmitteckert, K. Raedecke, D. Rheinert, S. Diebold, R. Roeth, B. Weiss, M. Granzow, B. Niesler, A. Griesbeck, et al.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms. 2021 April;1864(4-5):194702. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2021.194702.
Precise Correction of Heterozygous SHOX2 Mutations in hiPSCs Derived from Patients with Atrial Fibrillation via Genome Editing and Sib Selection.
S. A. Sumer*, S. Hoffmann*, S. Laue, B. Campbell, K. Raedecke, V. Frajs, S. Clauss, S. Kääb, J. W. Janssen, A. Jauch, et al.
Stem Cell Reports. 2020 October;15(4):999-1013. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.08.015.
Functional Characterization of Rare Variants in the SHOX2 Gene Identified in Sinus Node Dysfunction and Atrial Fibrillation.
S. Hoffmann, C. Paone, S. A. Sumer, S. Diebold, B. Weiss, R. Roeth, S. Clauss, I. Klier, S. Kääb, A. Schulz, et al.
Front. Genet.. 2019 Jul 11;10. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00648.
Murine transgenic embryonic stem cell lines for the investigation of sinoatrial node-related molecular pathways.
S. Schmitteckert, A. Griesbeck, S. Sumer, A. Jauch, A. Rolletschek, B. Niesler, G. A. Rappold, S. Hoffmann.
Stem Cell Research. 2017 December;25:278-282. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2017.07.011.
Comparative expression analysis of Shox2 -deficient embryonic stem cell-derived sinoatrial node-like cells.
S. Hoffmann*, S. Schmitteckert*, A. Griesbeck, H. Preiss, S. Sumer, A. Rolletschek, M. Granzow, V. Eckstein, B. Niesler, G. A. Rappold.
Stem Cell Research. 2017 May;21:51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2017.03.018.
Coding and non-coding variants in the SHOX2 gene in patients with early-onset atrial fibrillation.
S. Hoffmann, S. Clauss, I. M. Berger, B. Weiß, A. Montalbano, R. Röth, M. Bucher, I. Klier, R. Wakili, H. Seitz, et al.
Basic Res Cardiol. 2016 Apr 30;111(3). doi: 10.1007/s00395-016-0557-2.
Islet1 is a direct transcriptional target of the homeodomain transcription factor Shox2 and rescues the Shox2-mediated bradycardia.
S. Hoffmann, I. M. Berger, A. Glaser, C. Bacon, L. Li, N. Gretz, H. Steinbeisser, W. Rottbauer, S. Just, G. Rappold.
Basic Res Cardiol. 2013 March;108(2). doi: 10.1007/s00395-013-0339-z.
Shox2 mediates Tbx5 activity by regulating Bmp4 in the pacemaker region of the developing heart.
S. Puskaric (= S. Hoffmann), S. Schmitteckert, A. D. Mori, A. Glaser, K. U. Schneider, B. G. Bruneau, R. J. Blaschke, H. Steinbeisser, G. Rappold.
Human Molecular Genetics. 2010 Sep 21;19(23):4625-4633. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq393.
(* shared authorship)
- Section Nephrogenetics (AG Simons)
- Seniorprofessorship Prof. Rappold
- Molecular Neurogenetics (AG Berkel)
- Cardiogenetics (AG Hoffmann)
- Neurogastrogenetics
- Transcriptional regulation in developmental disorders (AG Laugsch)
- Genetics of neurodevelopmental disorders (AG Schaaf)
- Mouse models for neurodevelopmental disorders
- Research in our Diagnostic Laboratories
- Publications
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/8/2/csm_20131204_Beratung_035_a396c6c6e5.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/a/0/csm_20170627_PflegeOrtho_001_fb912471fa.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/f/c/csm_20170215_LaborOMZ_155_c0169c0898.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/2/c/csm_20180523_Labor_139_6ebb9a0a1b.jpg)

