Research group Dao Thi
Research projects in our group focus on "Hepatitis E Virus-Host Interactions using Stem Cell-Derived Culture Systems".
Projects
The Dao Thi lab uses stem cell-derived culture models to study hepatitis E virus (HEV). With about 20 million infections each year, leading to more than 3 million symptomatic cases and ~60000 fatalities, HEV is believed to be the most common cause of acute hepatitis in the world. Despite increasing awareness, HEV remains an understudied virus. A contributor to the poor understanding is the difficulty to propagate HEV in cell culture. To overcome these limitations, we use embryonic or induced pluripotent stem cell (hESC/iPSC)-derived cell culture models, in particular stem-cell derived hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs). Unlike conventionally used hepatoma cells, we found that HLCs are permissive for infection by primary isolates of all four HEV genotypes that can infect humans. HLCs therefore enable studies of authentic pan-genotype HEV biology. Further, the capability to study replication of non-adapted HEV isolates in tandem with autologous, patient-derived iPSCs enables personalized models of HEV infection and will serve as a platform for testing novel anti-HEV treatments (Figure 1).
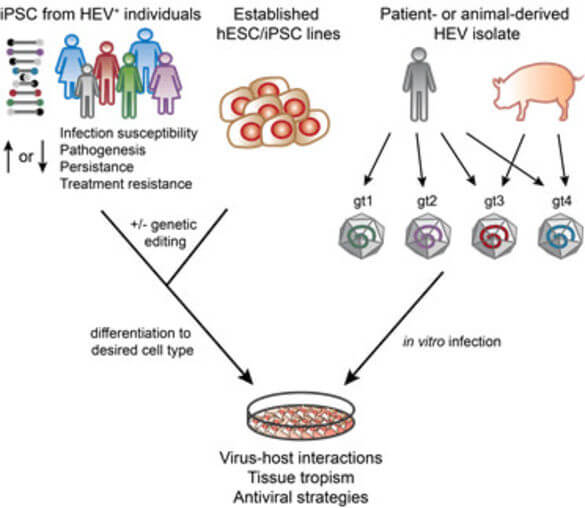
We also developed a novel stem cell-based differentiation protocol that uses transwell filters to generate columnar polarized HLCs. HEV is transmitted via the fecal-oral route and hepatocytes are similar to other epithelial cells polarized in vivo. In the absence of robust hepatocyte polarity systems our polarized HLC system now allows us to study directional HEV assembly and release, the final steps of the virus life cycle. Our studies aim at understanding different steps of the HEV life cycle with the overriding goal to identify new specific targets for therapeutic intervention.
Selected Publications
Complete Publication List (PubMed)
- Dao Thi VL, Herbst K, Boerner K, Meurer M, Kremer PML, Kirrmaier D, Freistaedter A, Papagiannidis D, Galmozzi C, Stanifer ML, Boulant S, Klein S, Chlanda P, Khalid D, Barreto Mirranda I, Schnitzler P, Kräusslich HG, Knop M, and Anders S (2020). A colorimetric RT-LAMP assay and LAMP-sequencing for detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA in clinical samples. Sci Transl Med. 12(556):eabc7075.
- Dao Thi VL, Wu X, Belote RL, Andreo U, Takacs CN, Fernandez JP, Vale-Silva LA, Decker CC, Fu RM, Qu B, Uryu K, Molina H, Saeed M, Steinmann E, Urban S, Singarja RR, Schneider WM, Simon SM, and Rice CM (2020). Stem cell-derived polarized hepatocytes. Nature Commun. 11(1):1677.
- Fu RM, Decker CC, and Dao Thi VL (2019). Cell Culture Models for Hepatitis E Virus. Viruses 11(7):608.
- Wu X*, Dao Thi VL*, Liu P, Takacs CN, Xiang K, Andrus L, Gouttenoire J, Moradpour D, and Rice CM (2018). Pan-Genotype Hepatitis E Virus Replication in Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocellular Systems. Gastroenterology. 154(3):663-647
- Wu X, Dao Thi VL, Huang Y, Billerbeck E, Saha D, Hoffmann HH, Wang Y, Vale Silva LA, Sarbanes S, Sun T, Andrus L, Quirk C, MacDonald MR, Schneider WM, An X, Rosenberg BR, and Rice CM. Intrinsic Immunity Shapes Viral Resistance of Stem Cells (2018). Cell. 172(3):423-438
Group Members
- Dr. Viet Loan Dao Thi, Principal Investigator
vietloan.daothi(at)med.uni-heidelberg.de
CIID Room 041, +49 6221 56-7865
- Patrick Bröscky, PhD Student
patrick.broescky(at)med.uni-heidelberg.de
CIID Room 002, +49 6221 56-7858
- Huanting Chi, PhD Student
huanting.chi(at)med.uni-heidelberg.de
CIID Room 002, +49 6221 56-7858
- Charlotte Decker, PhD Student
charlotte.decker(at)med.uni-heidelberg.de
CIID Room 002, +49 6221 56-7858
- Andrew Freistaedter, Lab Manager
andrew.freistaedter(at)med.uni-heidelberg.de
CIID Room 002b, +49 6221 56-7869
- Rebecca Fu, PhD Student
rebecca.fu(at)med.uni-heidelberg.de
CIID Room 002, +49 6221 56-7858
- Jun-Gen Hu, PhD Student
CIID Room 002, +49 6221 56-7858
- Ann-Kathrin Mehnert, PhD Student
ann-kathrin.mehnert(at)med.uni-heidelberg.de
CIID Room 002, +49 6221 56-7858
- Ashim Sahu, PhD Student
ashim.sahu2(at)med.uni-heidelberg.de
CIID Room 002, +49 6221 56-7858
Alumni
Former Lab Members
- Guglielmo Bove
- Lars Maurer
- Paul Park
- Cindy Zhang
Group Leader
For more information about the Dao Thi Lab, please check out Website Dao Thi Lab
This group is located on the 3rd floor of the Center for Integrative Infectious Disease Research (CIID) at INF 344 and supported by the Chica and Heinz Schaller Foundation Heidelberg


