Research Clinical Pharmacy
From practice for practice
The hospital pharmacy at Heidelberg University Hospital acts as a competent point of contact for the entire spectrum of pharmaceutical sciences at Heidelberg University Hospital. In all areas, the focus is on the close integration of routine inpatient care and pharmaceutical research in order to enable safe and effective drug therapy for patients at Heidelberg University Hospital (UKHD).
The identification of risky steps in the routine medication process for which customised measures and solutions are developed, implemented, evaluated and ultimately successfully consolidated in routine care in the specific BEDSIDE, BENCH and MANUFACTURING departments is central to this.
The hospital pharmacy is part of the drug therapy safety cluster (AMTS), which aims to improve the quality of drug therapy at UKHD.
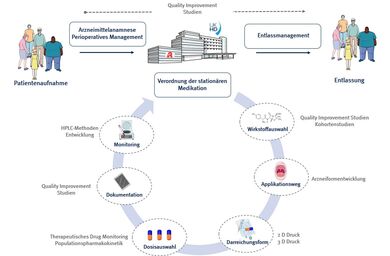
BENCH
The BENCH experimental area focusses on the development of HPLC methods that enable easy-to-implement determination of drug concentrations in routine applications. On the one hand, these can provide the basis for population pharmacokinetic analyses; on the other hand, they can be used to determine drug concentrations in the blood as part of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) in order to individualise dosages for special patient populations, such as patients in intensive care units with impaired kidney function.
BEDSIDE
The BEDSIDE department is closely linked to the clinical-pharmaceutical services provided by the ward pharmacists, who are an integral part of the treatment teams at many UKHD clinics with their drug anamnesis, ward round support and pharmacotherapeutic counselling, drug information and discharge management services. The aim of these activities is to ensure safe and effective drug therapy for UKHD patients.
To this end, the BEDSIDE department develops and implements practical solutions for drug-related risks and improvement potential identified in routine practice and measures their effects in routine practice in order to continuously and sustainably improve the quality of drug care.
CO-OPERATION PARTNER
In our experience, optimal quality in drug therapy can be achieved particularly when the various professional groups in the medication process work together interprofessionally and contribute their respective perspectives. We also pursue this approach in research, so that a large number of projects are planned and successfully implemented on an interprofessional basis together with co-operation partners.
If you are interested in working with us, we look forward to hearing from you.
At the UKHD and the University Campus:
Clinic for Anaesthesiology, Prof. Dr Markus Weigand,
Infectiology and Tropical Medicine, Prof Dr Claudia Denkinger, Dr Elham Khatamzas
Clinical Microbiology and Hygiene, PD Dr Sabrina Klein
Department of Haemato-oncology, Prof. Dr Carsten Müller-Tidow
Clinic for Cardiac Surgery, Prof Dr Matthias Karck
Clinic for Cardiology, Prof Dr C. Schmidt
Clinical Pharmacology and Epidemiology, Prof. Dr Walter E. Haefeli, Prof. Dr Hanna Seidling
External partners:
LMU Munich, PD Dr Uwe Liebchen
University of Hamburg, Prof Dr Sebastian Wicha
Heidenheim Hospital, Dr Otto Frey/Prof. Dr Alexander Brinkmann
Translational Cardiology, Kiel University Hospital, Prof Dr Oliver Müller
Promotion
In the hospital pharmacy, successful and in some cases award-winning doctoral theses have been carried out and the opportunity to do a doctorate is still offered. If no positions are advertised, you are still welcome to contact us if you are interested.
Practical year
As part of the practical year, we offer our PJ students the opportunity to work on research projects and gain an initial insight into scientific work. If you are interested in doing part of your practical year entirely in the field of research, you are welcome to contact us directly. This can be an advantage if you are aiming for a doctorate in the field of clinical pharmacy.
Publications
Publications and work from the hospital pharmacy can be accessed via the following link.
Awards and honours
Research papers and doctoral theses from the hospital pharmacy have been repeatedly honoured in the past.
ADKA Poster Prize 2024, 1st place
"Learning progress of artificial intelligence in answering clinical-pharmaceutical questions"
ADKA Innovation Award 2023
"Perioperative medication management rethought - a multimodal toolkit for the intersectoral improvement of perioperative medication management"
EAHP Poster Prize 2022
"Implementation of an interprofessional pre-operative medication management programme in cardiac surgery - a pre post quality improvement study"
ADKA Doctoral Prize 2021
"Revival of phyostigmine - A randomized , double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study on the adjunctive use of physostigmine salicylate in perioperative septic shock" Dr Nadine Pinder
ADKA doctoral prize 2020
"Development, selection and implementation of various elements to improve the discharge management of inpatients" Dr Benedict Morath
ADKA doctoral prize 2017
"Investigation of the efficacy and safety of antibiotic therapy in patients with evidence of valvular endocarditis" Dr Tobias Borst
ADKA Innovation Award 2013
"Off-label use in oncology - algorithm for prescribing chemotherapy"
![[Translate to English:] Portrait von Dr. Benedict Morath [Translate to English:] Portrait von Dr. Benedict Morath](/fileadmin/_processed_/1/9/csm_Morath__Benedict_DSC4532_79e16add4d.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] Portrait von Dr. Ute Chiriac [Translate to English:] Portrait von Dr. Ute Chiriac](/fileadmin/_processed_/d/9/csm_blassmann_ute_2017_04_347f3425f3.jpg)